Workshop 9.8b - Mixed effects (multilevel models): Randomized block and repeated measures designs (Bayesian)
23 April 2011
Randomized block and simple repeated measures ANOVA (Mixed effects) references
- McCarthy (2007) - Chpt ?
- Kery (2010) - Chpt ?
- Gelman & Hill (2007) - Chpt ?
- Logan (2010) - Chpt 13
- Quinn & Keough (2002) - Chpt 10
> library(R2jags) > library(ggplot2) > library(grid) > #define my common ggplot options > murray_opts <- opts(panel.grid.major=theme_blank(), + panel.grid.minor=theme_blank(), + panel.border = theme_blank(), + panel.background = theme_blank(), + axis.title.y=theme_text(size=15, vjust=0,angle=90), + axis.text.y=theme_text(size=12), + axis.title.x=theme_text(size=15, vjust=-1), + axis.text.x=theme_text(size=12), + axis.line = theme_segment(), + legend.position=c(1,0.1),legend.justification=c(1,0), + legend.key=theme_blank(), + plot.margin=unit(c(0.5,0.5,1,2),"lines") + ) > > #create a convenience function for predicting from mcmc objects > predict.mcmc <- function(mcmc, terms=NULL, mmat, trans="identity") { + library(plyr) + library(coda) + if(is.null(terms)) mcmc.coefs <- mcmc + else { + iCol<-match(terms, colnames(mcmc)) + mcmc.coefs <- mcmc[,iCol] + } + t2=")" + if (trans=="identity") { + t1 <- "" + t2="" + }else if (trans=="log") { + t1="exp(" + }else if (trans=="log10") { + t1="10^(" + }else if (trans=="sqrt") { + t1="(" + t2=")^2" + } + eval(parse(text=paste("mcmc.sum <-adply(mcmc.coefs %*% t(mmat),2,function(x) { data.frame(mean=",t1,"mean(x)",t2,", median=",t1,"median(x)",t2,", ",t1,"coda:::HPDinterval(as.mcmc(x), p=0.68)",t2,", ",t1,"coda:::HPDinterval(as.mcmc(x))",t2," )})", sep=""))) + + mcmc.sum + } > > > #create a convenience function for summarizing mcmc objects > summary.mcmc <- function(mcmc, terms=NULL, trans="identity") { + library(plyr) + library(coda) + if(is.null(terms)) mcmc.coefs <- mcmc + else { + iCol<-grep(terms, colnames(mcmc)) + mcmc.coefs <- mcmc[,iCol] + } + t2=")" + if (trans=="identity") { + t1 <- "" + t2="" + }else if (trans=="log") { + t1="exp(" + }else if (trans=="log10") { + t1="10^(" + }else if (trans=="sqrt") { + t1="(" + t2=")^2" + } + eval(parse(text=paste("mcmc.sum <-adply(mcmc.coefs,2,function(x) { data.frame(mean=",t1,"mean(x)",t2,", median=",t1,"median(x)",t2,", ",t1,"coda:::HPDinterval(as.mcmc(x), p=0.68)",t2,", ",t1,"coda:::HPDinterval(as.mcmc(x))",t2," )})", sep=""))) + + mcmc.sum$Perc <-100*mcmc.sum$median/sum(mcmc.sum$median) + mcmc.sum + }
Randomized block design
A plant pathologist wanted to examine the effects of two different strengths of tobacco virus on the number of lesions on tobacco leaves. She knew from pilot studies that leaves were inherently very variable in response to the virus. In an attempt to account for this leaf to leaf variability, both treatments were applied to each leaf. Eight individual leaves were divided in half, with half of each leaf inoculated with weak strength virus and the other half inoculated with strong virus. So the leaves were blocks and each treatment was represented once in each block. A completely randomised design would have had 16 leaves, with 8 whole leaves randomly allocated to each treatment.
Download Tobacco data set
| Format of tobacco.csv data files | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
 |
Open the tobacco data file.
> tobacco <- read.table("../downloads/data/tobacco.csv", + header = T, sep = ",", strip.white = T) > head(tobacco)
LEAF TREATMENT NUMBER 1 L1 Strong 35.90 2 L1 Weak 25.02 3 L2 Strong 34.12 4 L2 Weak 23.17 5 L3 Strong 35.70 6 L3 Weak 24.12
To appreciate the difference between this design (Complete Randomized Block) in which there is a single within Group effect (Treatment) and a nested design (in which there are between group effects), I will illustrate the current design diagramatically.
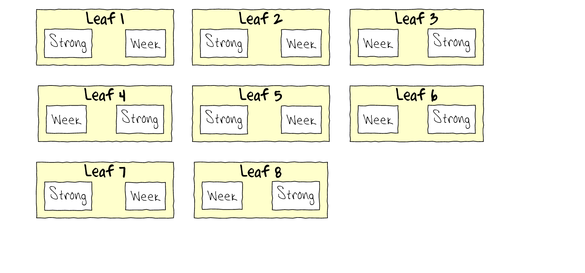
- Note that each level of the Treatment (Strong and Week) are applied to each Leaf (Block)
- Note that Treatments are randomly applied
- The Treatment effect is the mean difference between Treatment pairs per leaf
- Blocking in this way is very useful when spatial or temporal heterogeneity is likely to add noise that could make it difficualt to detect a difference between Treatments. Hence it is a way of experimentally reducing unexplained variation (compared to nesting which involves statistical reduction of unexplained variation).
Exploratory data analysis has indicated that the response variable could be normalized via a forth-root transformation.
- Fit the JAGS model for the Randomized Complete Block
- Effects parameterization - random intercepts model
number of lesionsi = βSite j(i) + εi where ε ∼ N(0,σ2)
View full code> runif(1)
[1] 0.7823
> modelString=" model { #Likelihood for (i in 1:n) { number[i]~dnorm(mean[i],tau.res) mean[i] <- beta.leaf[leaf[i]]+beta.treatment[treatment[i]] y.err[i] <- number[i] - mean[1] } #Priors and derivatives #alpha ~ dnorm(0,1.0E-6) #beta.leaf[1] <- 0 for (i in 1:nLeaf) { beta.leaf[i] ~ dnorm(0,1.0E-6) } beta.treatment[1] <- 0 for (i in 2:nTreat) { beta.treatment[i] ~ dnorm(0,1.0E-6) } Treatment.means[1] <- beta.leaf[1]+beta.treatment[1] Treatment.means[2] <- beta.leaf[1]+beta.treatment[2] tau.res <- pow(sigma.res,2) #sigma.res ~ dgamma(0.001,0.001) sigma.res ~ dunif(0,100) sd.Leaf <- sd(beta.leaf) sd.Treatment <- sd(beta.treatment) sd.Resid <- sd(y.err) perc.Treat <- 100*beta.treatment[2]/(Treatment.means[1]+1.0E-10) p.decline <- 1-step(beta.treatment[2]) p.decline5 <- 1-step(beta.treatment[2]+Treatment.means[1]*0.05) p.decline10 <- 1-step(beta.treatment[2]+Treatment.means[1]*0.1) p.decline20 <- 1-step(beta.treatment[2]+Treatment.means[1]*0.2) p.decline50 <- 1-step(beta.treatment[2]+Treatment.means[1]*0.5) p.decline100 <- 1-step(beta.treatment[2]+Treatment.means[1]*1) } " > ## write the model to a text file (I suggest you alter the path to somewhere more relevant > ## to your system!) > writeLines(modelString,con="../downloads/BUGSscripts/ws9.8bQ1.1a.txt") > tobacco.list <- with(tobacco, + list(number=NUMBER, + treatment=as.numeric(TREATMENT), + leaf=as.numeric(LEAF), + n=nrow(tobacco), nTreat=length(levels(as.factor(TREATMENT))), + nLeaf=length(levels(as.factor(LEAF))) + ) + ) > params <- c("perc.Treat","p.decline","p.decline5","p.decline10","p.decline20","p.decline50","p.decline100","Treatment.means","beta.leaf","beta.treatment","sigma.res","sd.Resid","sd.Leaf","sd.Treatment") > adaptSteps = 1000 > burnInSteps = 200 > nChains = 3 > numSavedSteps = 5000 > thinSteps = 10 > nIter = ceiling((numSavedSteps * thinSteps)/nChains) > > library(R2jags) > ## > tobacco.r2jags <- jags(data=tobacco.list, + inits=NULL,#inits=list(inits,inits,inits), # since there are three chains + parameters.to.save=params, + model.file="../downloads/BUGSscripts/ws9.8bQ1.1a.txt", + n.chains=3, + n.iter=nIter, + n.burnin=burnInSteps, + n.thin=thinSteps + )
Compiling model graph Resolving undeclared variables Allocating nodes Graph Size: 136 Initializing model
> print(tobacco.r2jags)
Inference for Bugs model at "../downloads/BUGSscripts/ws9.8bQ1.1a.txt", fit using jags, 3 chains, each with 16667 iterations (first 200 discarded), n.thin = 10 n.sims = 4941 iterations saved mu.vect sd.vect 2.5% 25% 50% 75% 97.5% Rhat n.eff Treatment.means[1] 34.379 3.164 27.938 32.499 34.377 36.352 40.616 1.002 2000 Treatment.means[2] 26.487 3.181 20.064 24.520 26.475 28.379 32.827 1.001 4000 beta.leaf[1] 34.379 3.164 27.938 32.499 34.377 36.352 40.616 1.002 2000 beta.leaf[2] 32.623 3.095 26.524 30.717 32.587 34.552 38.757 1.001 4900 beta.leaf[3] 33.857 3.116 27.603 31.929 33.815 35.730 40.144 1.001 4900 beta.leaf[4] 31.068 3.107 24.612 29.226 31.111 32.969 37.351 1.001 4900 beta.leaf[5] 32.997 3.038 26.917 31.137 32.963 34.943 39.039 1.001 4900 beta.leaf[6] 40.299 3.061 34.320 38.404 40.275 42.178 46.359 1.001 2900 beta.leaf[7] 43.514 3.080 37.218 41.663 43.517 45.461 49.468 1.001 4900 beta.leaf[8] 30.853 3.126 24.595 28.938 30.819 32.776 37.179 1.001 4900 beta.treatment[1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.treatment[2] -7.893 2.084 -12.000 -9.158 -7.929 -6.646 -3.635 1.001 4900 p.decline 0.999 0.032 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.189 1900 p.decline10 0.980 0.139 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.005 4900 p.decline100 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 p.decline20 0.722 0.448 0.000 0.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.002 2300 p.decline5 0.995 0.071 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.033 2900 p.decline50 0.000 0.014 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.291 4900 perc.Treat -22.974 5.812 -34.315 -26.492 -23.019 -19.543 -11.027 1.001 4900 sd.Leaf 4.950 1.021 3.169 4.261 4.882 5.541 7.192 1.001 4900 sd.Resid 6.333 0.000 6.333 6.333 6.333 6.333 6.333 1.000 1 sd.Treatment 3.948 1.034 1.829 3.323 3.964 4.579 6.000 1.007 3900 sigma.res 0.272 0.069 0.147 0.223 0.268 0.318 0.414 1.001 4900 deviance 89.239 6.593 79.379 84.361 88.234 93.076 104.436 1.001 4900 For each parameter, n.eff is a crude measure of effective sample size, and Rhat is the potential scale reduction factor (at convergence, Rhat=1). DIC info (using the rule, pD = var(deviance)/2) pD = 21.7 and DIC = 111.0 DIC is an estimate of expected predictive error (lower deviance is better).Note that the Leaf β are not actually the leaf means. Rather they are the intercepts for each leaf (since we have fit a random intercepts model). They represent the value of the first Treatment level (Strong) within each Leaf.
The Treatment effect thus represents the mean of the differences between the second Treatment level (Week) and these intercepts.
Indeed, the analysis assumes that there is no real interactions between the Leafs (Blocks) and the Treatment effects (within Blocks) - otherwise the mean Treatment effect would be a over simplification of the true nature of the populations. The presence of such an interaction would indicate that the Blocks (Leafs) do not all represent the same population.
If we really want to explore whether there are Block by within block effects or obtain Leaf means that reflected the means of both levels of the Treatment, we can fit the full multiplicative model (random intercept and slope) and explore the marginal effects and interactions.View full code> runif(1)
[1] 0.8945
> modelString=" model { #Likelihood for (i in 1:n) { number[i]~dnorm(mean[i],tau.res) mean[i] <- beta[leaf[i],treatment[i]] y.err[i] <- number[i] - mean[1] } #Priors and derivatives for (i in 1:nLeaf) { for (j in 1:nTreat) { beta[i,j] ~ dnorm(0,1.0E-6) } } #Effects beta0 <- beta[1,1] for (i in 1:nLeaf) { beta.leaf[i] <- mean(beta[i,]-beta[1,]) } #Leaf.means[1] <- mean(beta[1,]) for (i in 1:nLeaf) { Leaf.means[i] <- mean(beta[i,]) } for (i in 1:nTreat) { beta.treatment[i] <- mean(beta[,i]-beta[,1]) } for (i in 1:nTreat) { Treatment.means[i] <- mean(beta[,i]) } for (i in 1:nLeaf){ for (j in 1:nTreat){ beta.int[i,j] <- beta[i,j]-beta.leaf[i]-beta.treatment[j]-beta0 } } tau.res <- pow(sigma.res,2) #sigma.res ~ dgamma(0.001,0.001) sigma.res ~ dunif(0,100) sd.Leaf <- sd(Leaf.means) sd.Treatment <- sd(Treatment.means) sd.Int <- sd(beta.int[,]) sd.Resid <- sd(y.err) } " > ## write the model to a text file (I suggest you alter the path to somewhere more relevant > ## to your system!) > writeLines(modelString,con="../downloads/BUGSscripts/ws9.8bQ1.1b.txt") > tobacco.list <- with(tobacco, + list(number=NUMBER, + treatment=as.numeric(TREATMENT), + leaf=as.numeric(LEAF), + n=nrow(tobacco), nTreat=length(levels(as.factor(TREATMENT))), + nLeaf=length(levels(as.factor(LEAF))) + ) + ) > params <- c("Leaf.means","Treatment.means","beta","beta.leaf","beta.treatment","sigma.res","sd.Leaf","sd.Treatment","sd.Int","sd.Resid") > adaptSteps = 1000 > burnInSteps = 200 > nChains = 3 > numSavedSteps = 5000 > thinSteps = 10 > nIter = ceiling((numSavedSteps * thinSteps)/nChains) > > library(R2jags) > ## > tobacco.r2jags2 <- jags(data=tobacco.list, + inits=NULL,#inits=list(inits,inits,inits), # since there are three chains + parameters.to.save=params, + model.file="../downloads/BUGSscripts/ws9.8bQ1.1b.txt", + n.chains=3, + n.iter=nIter, + n.burnin=burnInSteps, + n.thin=thinSteps + )
Compiling model graph Resolving undeclared variables Allocating nodes Graph Size: 185 Initializing model
> print(tobacco.r2jags2)
Inference for Bugs model at "../downloads/BUGSscripts/ws9.8bQ1.1b.txt", fit using jags, 3 chains, each with 16667 iterations (first 200 discarded), n.thin = 10 n.sims = 4941 iterations saved mu.vect sd.vect 2.5% 25% 50% 75% 97.5% Rhat n.eff Leaf.means[1] 30.456 1.841 30.362 30.449 30.459 30.469 30.568 1.289 4900 Leaf.means[2] 28.659 1.462 28.524 28.633 28.643 28.653 28.741 1.288 4900 Leaf.means[3] 29.880 2.837 29.809 29.902 29.912 29.922 30.007 1.290 4900 Leaf.means[4] 27.125 2.627 26.970 27.072 27.082 27.092 27.198 1.288 4900 Leaf.means[5] 29.097 2.137 28.996 29.093 29.103 29.112 29.206 1.288 4900 Leaf.means[6] 36.331 3.032 36.257 36.351 36.361 36.370 36.470 1.290 4900 Leaf.means[7] 39.578 1.313 39.498 39.594 39.604 39.614 39.696 1.286 3600 Leaf.means[8] 26.810 2.170 26.743 26.830 26.841 26.851 26.951 1.290 4600 Treatment.means[1] 34.916 1.487 34.888 34.935 34.940 34.945 34.993 1.291 4000 Treatment.means[2] 27.068 0.651 27.007 27.056 27.061 27.066 27.109 1.289 4900 beta[1,1] 35.871 1.870 35.754 35.884 35.898 35.912 36.054 1.289 3800 beta[2,1] 34.147 2.085 33.954 34.103 34.118 34.132 34.249 1.289 4500 beta[3,1] 35.638 3.459 35.551 35.688 35.702 35.717 35.843 1.290 3400 beta[4,1] 26.217 2.066 26.072 26.210 26.225 26.239 26.390 1.289 4900 beta[5,1] 33.011 4.340 32.871 33.003 33.017 33.030 33.156 1.290 4900 beta[6,1] 36.675 5.364 36.588 36.714 36.729 36.743 36.906 1.290 4900 beta[7,1] 44.708 1.798 44.549 44.709 44.724 44.737 44.859 1.288 4900 beta[8,1] 33.063 2.284 32.959 33.095 33.110 33.124 33.255 1.290 2300 beta[1,2] 25.040 2.420 24.880 25.006 25.020 25.034 25.154 1.289 4900 beta[2,2] 23.171 1.631 23.017 23.153 23.167 23.182 23.313 1.287 4900 beta[3,2] 24.121 2.872 23.971 24.108 24.122 24.136 24.252 1.290 4900 beta[4,2] 28.033 4.857 27.778 27.925 27.939 27.953 28.082 1.289 4900 beta[5,2] 25.183 1.865 25.039 25.175 25.189 25.203 25.324 1.285 4900 beta[6,2] 35.987 1.457 35.842 35.979 35.993 36.007 36.152 1.288 4900 beta[7,2] 34.449 2.620 34.332 34.470 34.485 34.499 34.624 1.287 4900 beta[8,2] 20.557 3.206 20.438 20.557 20.572 20.586 20.712 1.290 4900 beta.leaf[1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.leaf[2] -1.797 2.811 -1.969 -1.831 -1.817 -1.803 -1.696 1.290 4900 beta.leaf[3] -0.576 3.385 -0.707 -0.561 -0.547 -0.533 -0.402 1.290 4900 beta.leaf[4] -3.331 3.589 -3.530 -3.392 -3.377 -3.364 -3.218 1.290 4900 beta.leaf[5] -1.358 1.818 -1.489 -1.370 -1.357 -1.342 -1.215 1.288 4900 beta.leaf[6] 5.876 3.090 5.756 5.888 5.901 5.915 6.058 1.290 4900 beta.leaf[7] 9.123 1.483 9.004 9.130 9.145 9.158 9.277 1.283 4900 beta.leaf[8] -3.646 2.182 -3.771 -3.633 -3.618 -3.604 -3.473 1.290 4900 beta.treatment[1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.treatment[2] -7.849 1.438 -7.962 -7.886 -7.879 -7.872 -7.810 1.291 2300 sd.Int 2.599 1.726 2.485 2.512 2.516 2.519 2.563 1.290 240 sd.Leaf 4.345 1.886 4.243 4.269 4.273 4.277 4.320 1.294 290 sd.Resid 6.333 0.000 6.333 6.333 6.333 6.333 6.333 1.000 1 sd.Treatment 3.954 0.531 3.908 3.936 3.940 3.943 3.982 1.285 2300 sigma.res 51.752 28.688 2.331 27.783 52.065 76.524 97.783 1.052 140 deviance -71.200 33.611 -105.396 -93.245 -80.673 -60.124 17.555 1.051 140 For each parameter, n.eff is a crude measure of effective sample size, and Rhat is the potential scale reduction factor (at convergence, Rhat=1). DIC info (using the rule, pD = var(deviance)/2) pD = 556.9 and DIC = 485.7 DIC is an estimate of expected predictive error (lower deviance is better).View full code> runif(1)
[1] 0.34
> modelString=" model { #Likelihood for (i in 1:n) { number[i]~dnorm(mean[i],tau.res) mean[i] <- alpha+beta.leaf[leaf[i]] + beta.treatment[treatment[i]] + beta.int[leaf[i],treatment[i]] y.err[i] <- number[i] - mean[1] } #Priors and derivatives alpha ~ dnorm(0,1.0E-6) beta.leaf[1] <- 0 beta.int[1,1] <- 0 for (i in 2:nLeaf) { beta.leaf[i] ~ dnorm(0,1.0E-6) beta.int[i,1] <-0 } beta.treatment[1] <- 0 for (i in 2:nTreat) { beta.treatment[i] ~ dnorm(0,1.0E-6) beta.int[1,i] <- 0 } for (i in 2:nLeaf) { for (j in 2:nTreat) { beta.int[i,j] ~ dnorm(0,1.0E-6) } } tau.res <- pow(sigma.res,2) #sigma.res ~ dgamma(0.001,0.001) sigma.res ~ dunif(0,100) } " > ## write the model to a text file (I suggest you alter the path to somewhere more relevant > ## to your system!) > writeLines(modelString,con="../downloads/BUGSscripts/ws9.8bQ1.1c.txt") > tobacco.list <- with(tobacco, + list(number=NUMBER, + treatment=as.numeric(TREATMENT), + leaf=as.numeric(LEAF), + n=nrow(tobacco), nTreat=length(levels(as.factor(TREATMENT))), + nLeaf=length(levels(as.factor(LEAF))) + ) + ) > params <- c("alpha","beta.leaf","beta.treatment","beta.int","sigma.res") > adaptSteps = 1000 > burnInSteps = 200 > nChains = 3 > numSavedSteps = 5000 > thinSteps = 10 > nIter = ceiling((numSavedSteps * thinSteps)/nChains) > > library(R2jags) > ## > tobacco.r2jags3 <- jags(data=tobacco.list, + inits=NULL,#inits=list(inits,inits,inits), # since there are three chains + parameters.to.save=params, + model.file="../downloads/BUGSscripts/ws9.8bQ1.1c.txt", + n.chains=3, + n.iter=nIter, + n.burnin=burnInSteps, + n.thin=thinSteps + )
Compiling model graph Resolving undeclared variables Allocating nodes Graph Size: 116 Initializing model
> print(tobacco.r2jags3)
Inference for Bugs model at "../downloads/BUGSscripts/ws9.8bQ1.1c.txt", fit using jags, 3 chains, each with 16667 iterations (first 200 discarded), n.thin = 10 n.sims = 4941 iterations saved mu.vect sd.vect 2.5% 25% 50% 75% 97.5% Rhat n.eff alpha 35.878 1.255 35.734 35.883 35.897 35.911 36.048 1.234 1500 beta.int[1,1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.int[2,1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.int[3,1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.int[4,1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.int[5,1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.int[6,1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.int[7,1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.int[8,1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.int[1,2] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.int[2,2] -0.070 2.953 -0.431 -0.101 -0.073 -0.046 0.216 1.253 4900 beta.int[3,2] -0.657 2.908 -1.003 -0.732 -0.702 -0.675 -0.377 1.244 4900 beta.int[4,2] 12.574 2.514 12.226 12.564 12.592 12.619 12.859 1.219 4900 beta.int[5,2] 3.059 2.935 2.727 3.021 3.049 3.077 3.390 1.206 4900 beta.int[6,2] 10.083 3.013 9.831 10.112 10.142 10.170 10.445 1.209 2200 beta.int[7,2] 0.622 2.382 0.298 0.610 0.637 0.664 0.930 1.253 4900 beta.int[8,2] -1.697 2.309 -1.963 -1.689 -1.661 -1.634 -1.367 1.224 4900 beta.leaf[1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.leaf[2] -1.740 2.310 -2.005 -1.800 -1.780 -1.760 -1.537 1.254 1900 beta.leaf[3] -0.209 1.542 -0.425 -0.215 -0.195 -0.176 -0.003 1.186 4900 beta.leaf[4] -9.652 2.362 -9.871 -9.692 -9.673 -9.653 -9.429 1.232 4900 beta.leaf[5] -2.863 2.258 -3.080 -2.900 -2.881 -2.861 -2.643 1.240 3800 beta.leaf[6] 0.888 2.008 0.627 0.811 0.831 0.851 1.051 1.251 940 beta.leaf[7] 8.854 1.940 8.618 8.806 8.826 8.846 9.082 1.225 4200 beta.leaf[8] -2.761 1.544 -2.982 -2.807 -2.788 -2.768 -2.555 1.234 3500 beta.treatment[1] 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 1 beta.treatment[2] -10.882 1.871 -11.074 -10.896 -10.877 -10.857 -10.633 1.241 4900 sigma.res 52.309 29.008 2.121 27.030 54.293 77.575 97.780 1.021 220 deviance -71.311 34.429 -105.821 -93.649 -81.370 -59.776 21.548 1.021 210 For each parameter, n.eff is a crude measure of effective sample size, and Rhat is the potential scale reduction factor (at convergence, Rhat=1). DIC info (using the rule, pD = var(deviance)/2) pD = 587.3 and DIC = 516.0 DIC is an estimate of expected predictive error (lower deviance is better).In the above, alpha is the mean (value) of the Strong Treatment in Leaf 1. βTreatment 2 is the difference between the value of the Strong and Week Treatments in Leaf 1.
- Effects parameterization - random intercepts model
- Before fully exploring the parameters, it is prudent to examine the convergence and mixing diagnostics.
Chose either the effects or means parameterization model (they should yield much the same).
- Trace plots
View code
> plot(as.mcmc(tobacco.r2jags))
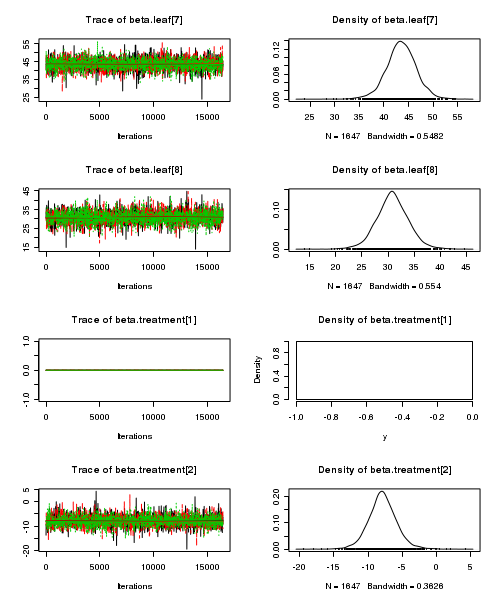
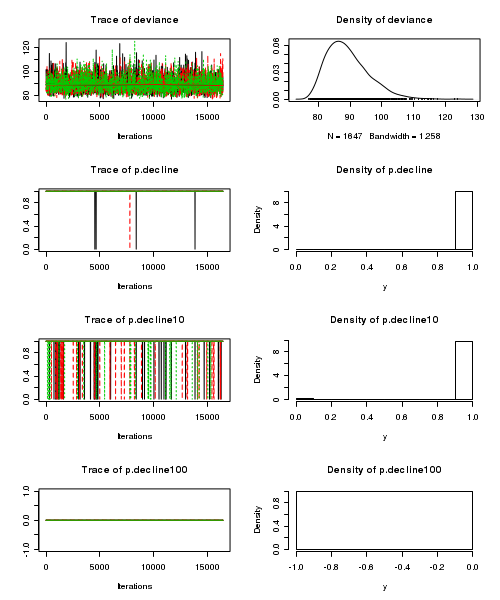
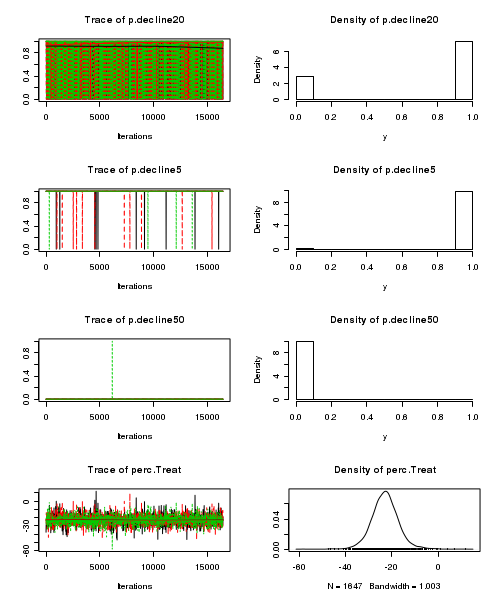
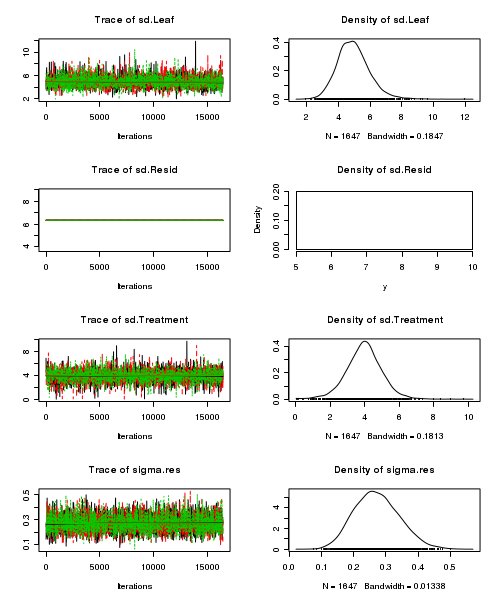
- Raftery diagnostic
View code
> raftery.diag(as.mcmc(tobacco.r2jags))
[[1]] Quantile (q) = 0.025 Accuracy (r) = +/- 0.005 Probability (s) = 0.95 You need a sample size of at least 3746 with these values of q, r and s [[2]] Quantile (q) = 0.025 Accuracy (r) = +/- 0.005 Probability (s) = 0.95 You need a sample size of at least 3746 with these values of q, r and s [[3]] Quantile (q) = 0.025 Accuracy (r) = +/- 0.005 Probability (s) = 0.95 You need a sample size of at least 3746 with these values of q, r and s
- Autocorrelation
View code
> autocorr.diag(as.mcmc(tobacco.r2jags))
Treatment.means[1] Treatment.means[2] beta.leaf[1] beta.leaf[2] beta.leaf[3] beta.leaf[4] Lag 0 1.0000000 1.000000 1.0000000 1.000000 1.000000 1.00000 Lag 10 0.0008802 0.006387 0.0008802 0.009082 0.010568 -0.02105 Lag 50 0.0163591 0.020910 0.0163591 -0.021316 0.006175 0.01663 Lag 100 0.0103684 0.014494 0.0103684 0.012102 0.004241 -0.01814 Lag 500 -0.0039647 0.006587 -0.0039647 0.006971 0.013273 -0.02884 beta.leaf[5] beta.leaf[6] beta.leaf[7] beta.leaf[8] beta.treatment[1] beta.treatment[2] Lag 0 1.000000 1.00000 1.0000000 1.000000 NaN 1.0000000 Lag 10 0.002638 -0.01812 0.0241051 0.017104 NaN 0.0047574 Lag 50 0.012203 -0.01305 -0.0051696 -0.003514 NaN -0.0114785 Lag 100 0.027296 -0.01367 -0.0222627 -0.011227 NaN -0.0003129 Lag 500 -0.009941 0.01217 0.0003319 0.020987 NaN -0.0041822 deviance p.decline p.decline10 p.decline100 p.decline20 p.decline5 p.decline50 perc.Treat Lag 0 1.000000 NaN 1.0000000 NaN 1.000000 1.000000 NaN 1.000000 Lag 10 0.009082 NaN -0.0008481 NaN 0.006289 -0.005092 NaN 0.006519 Lag 50 0.020272 NaN 0.0088339 NaN 0.014328 -0.005104 NaN -0.005918 Lag 100 -0.015875 NaN -0.0201543 NaN 0.008923 -0.005120 NaN 0.004018 Lag 500 -0.015573 NaN 0.0006197 NaN 0.017398 -0.004837 NaN 0.003894 sd.Leaf sd.Resid sd.Treatment sigma.res Lag 0 1.000000 NaN 1.000e+00 1.000000 Lag 10 0.005889 NaN 6.826e-03 0.036491 Lag 50 0.002473 NaN -1.070e-02 0.003780 Lag 100 -0.008857 NaN -5.059e-05 0.002928 Lag 500 0.025602 NaN -3.433e-03 0.012135
- Trace plots
-
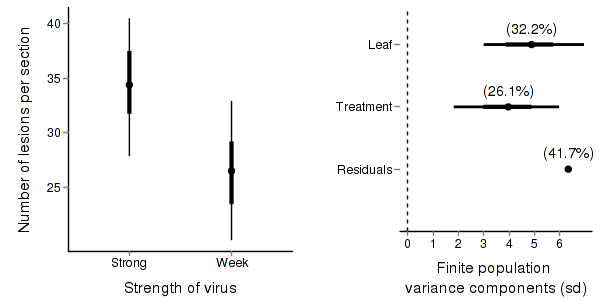
A summary figure would be nice
View code
> tobacco.mcmc <- as.mcmc(tobacco.r2jags$BUGSoutput$sims.matrix) > #get the column indexes for the parameters we are interested in > tobacco.sum <- summary.mcmc(tobacco.mcmc, terms=c("^Treatment")) > tobacco.sum$Treatment <- c("Strong","Week") > > p1<-ggplot(tobacco.sum,aes(y=mean, x=Treatment))+ + geom_errorbar(aes(ymin=lower, ymax=upper),width=0,size=1.5,position=position_dodge(0.2))+ + geom_errorbar(aes(ymin=lower.1, ymax=upper.1),width=0,position=position_dodge(0.2))+ + geom_point(size=3)+ + scale_y_continuous("Number of lesions per section")+ + scale_x_discrete("Strength of virus")+ + murray_opts > > > #Finite-population standard deviations > tobacco.sd <- summary.mcmc(tobacco.mcmc, terms=c("sd")) > rownames(tobacco.sd) <- c("Leaf", "Residuals", "Treatment") > tobacco.sd$name <- factor(c("Leaf", "Residuals", "Treatment"), levels=c("Residuals", "Treatment","Leaf")) > > p2<-ggplot(tobacco.sd,aes(y=name, x=median))+ + geom_vline(xintercept=0,linetype="dashed")+ + geom_hline(xintercept=0)+ + scale_x_continuous("Finite population \nvariance components (sd)")+ + geom_errorbarh(aes(xmin=lower.1, xmax=upper.1), height=0, size=1)+ + geom_errorbarh(aes(xmin=lower, xmax=upper), height=0, size=1.5)+ + geom_point(size=3)+ + geom_text(aes(label=sprintf("(%4.1f%%)",Perc),vjust=-1))+ + murray_opts+ + opts(axis.line=theme_blank(),axis.title.y=theme_blank(), + axis.text.y=theme_text(size=12,hjust=1)) > > grid.newpage() > pushViewport(viewport(layout=grid.layout(1,2,5,5,respect=TRUE))) > pushViewport(viewport(layout.pos.col=1, layout.pos.row=1)) > print(p1,newpage=FALSE) > popViewport(1) > pushViewport(viewport(layout.pos.col=2, layout.pos.row=1)) > print(p2,newpage=FALSE) > popViewport(0)